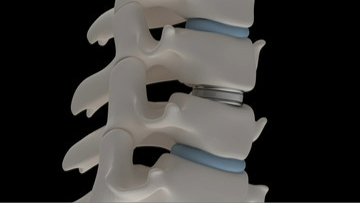
Cervical arthroplasty, also known as cervical disc arthroplasty or cervical ADR is a cutting-edge surgical procedure that has revolutionized the management of neck pain and disc disease.
Cervical arthroplasty, also known as cervical disc arthroplasty or cervical ADR is a cutting-edge surgical procedure that has revolutionized the management of neck pain and disc disease.
Every year, the month of October brings a special focus on an often overlooked but incredibly challenging health issue: facial pain. As Facial Pain Awareness Month begins, it’s the perfect time to bring attention to the challenging condition trigeminal neuralgia.
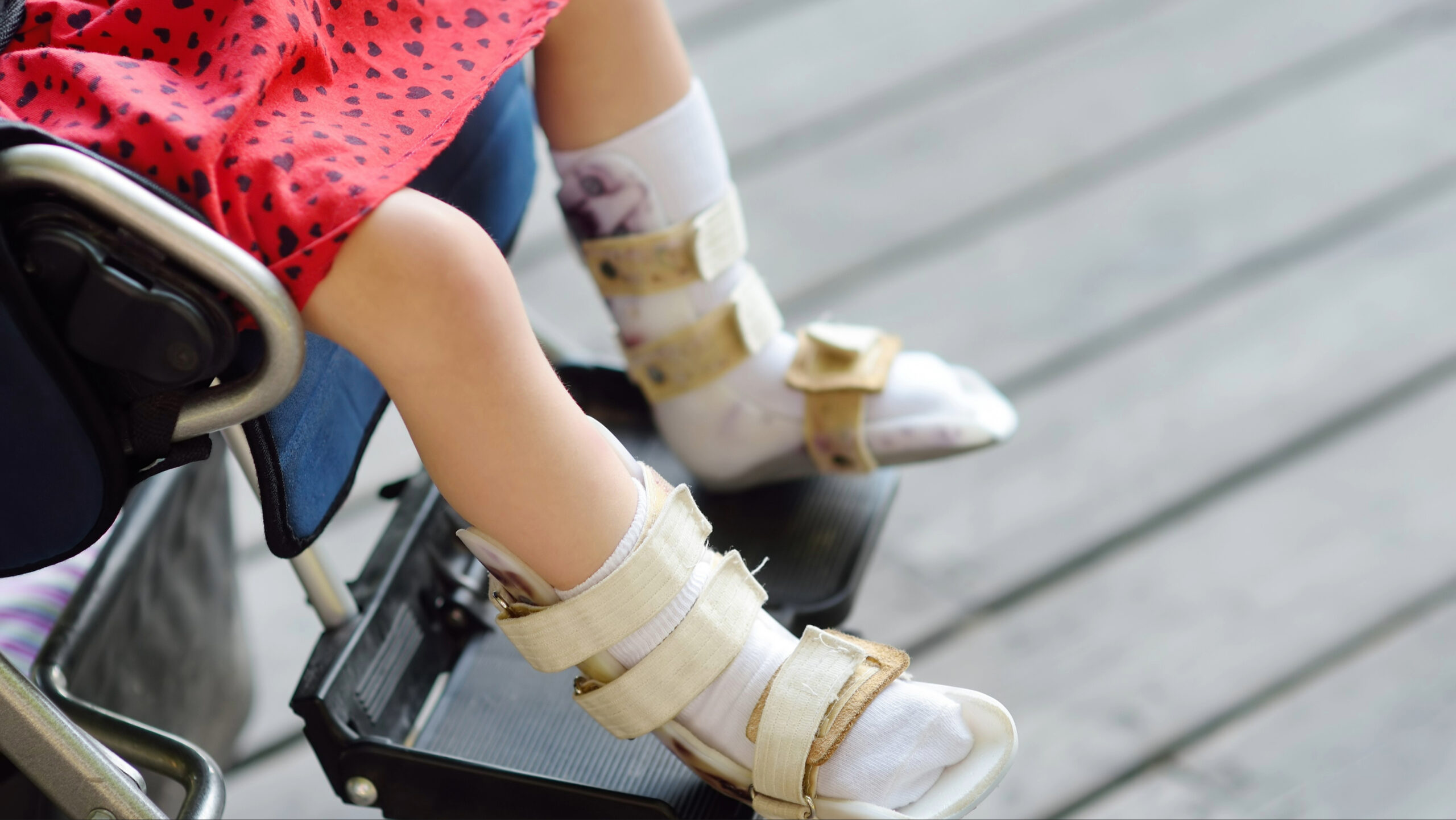
Not all children with cerebral palsy are candidates for SDR. Evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including a neurosurgeon, orthopedic surgeon, physiatrist, neurologist, physical therapist, and orthotist is best able to determine if SDR is the right treatment option for your child. Factors like age, severity and location of symptoms, and overall health will be considered.
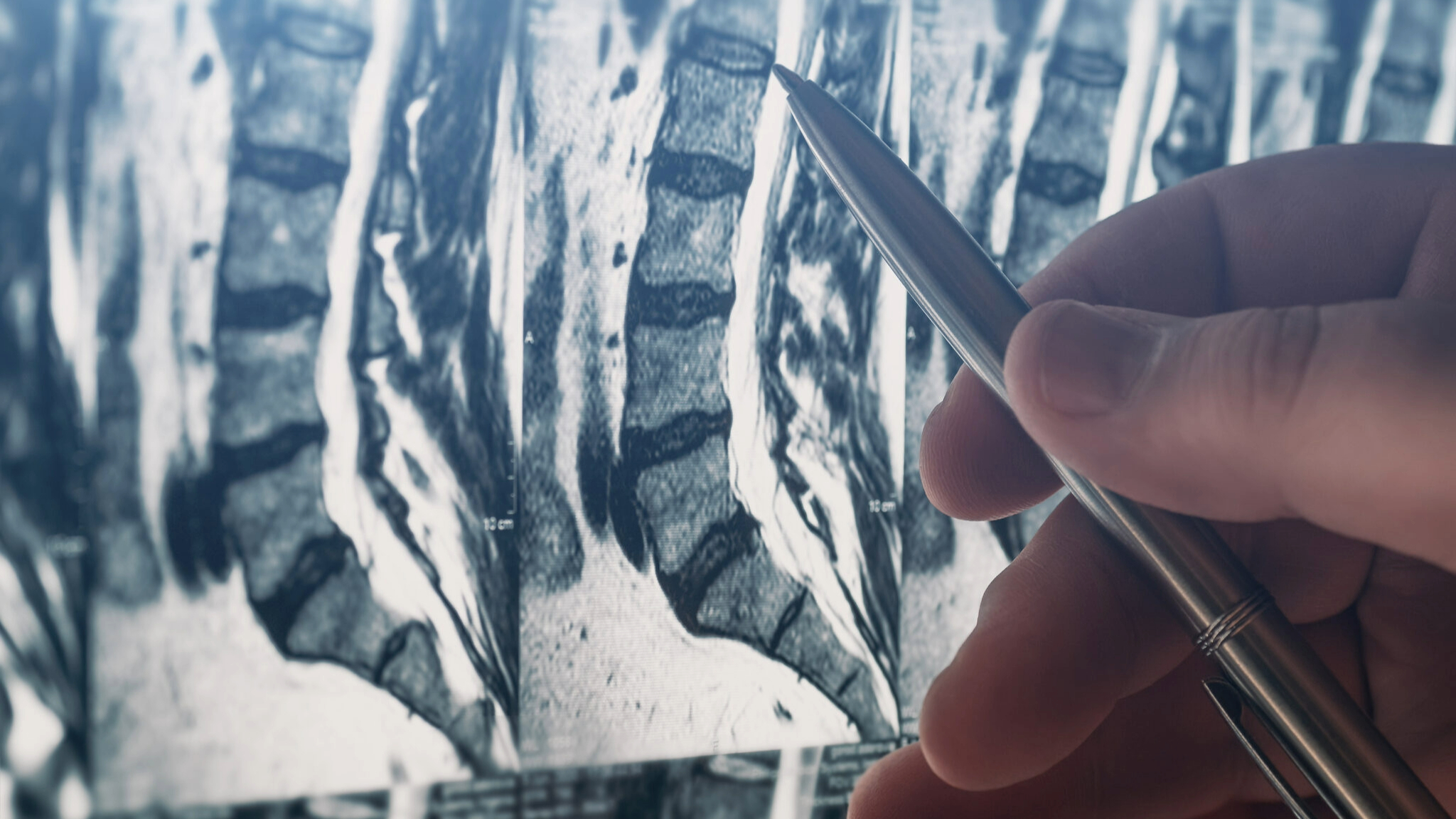
Lumbar decompression surgery is a surgical treatment designed to alleviate the pressure on the spinal cord or nerves in the lower back, particularly in cases of lumbar spinal stenosis, bone spurs, and other conditions that cause compression.
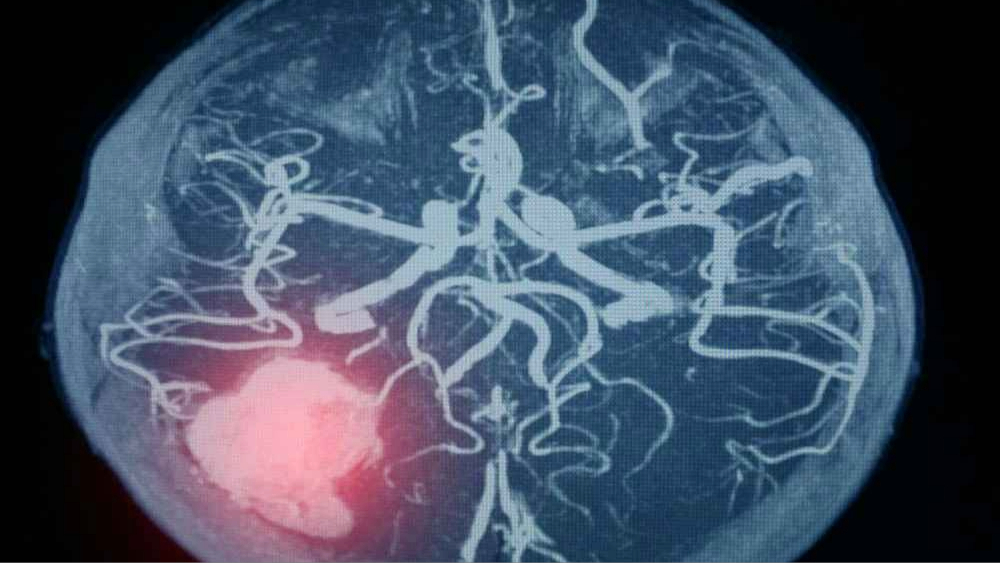
An unruptured brain aneurysm is a condition where a weakened area of a blood vessel in the brain forms a bulge or sac but has not yet burst or leaked. Unruptured aneurysms often do not cause any symptoms, which makes them challenging to detect. They are usually discovered incidentally during brain imaging scans performed for unrelated reasons.