About aneurysm coiling.
Brain aneurysms are blood filled bubbles that arise from an artery in the brain.
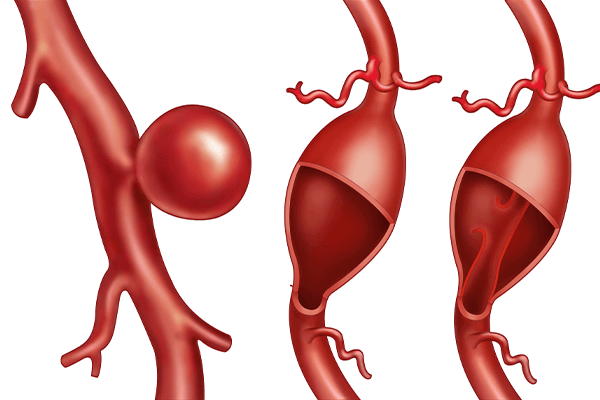
They are small outpouchings of a blood vessel caused by a weakness in the vessel wall. They look like a small grape or berry arising off a branch. They typically grow silently in the brain, and about 1 in 50 people carry them. Most people will never find out they are harboring a brain aneurysm, but with the development of newer advanced imaging techniques, doctors can now find out if a brain aneurysm is present. Often it gets diagnosed coincidentally when brain imaging is obtained for other reasons, for example after a car accident, or after a dizzy spell. Such an aneurysm is considered an unruptured aneurysm.
As the aneurysm grow, it may cause neurological symptoms such as headaches, vision loss etc. Doctors think that smoking cessation and good control blood pressure are the most common and modifiable risk factors that you can look after to prevent an aneurysm from growing or even bursting.
If you have a family history of brain aneurysms, ask your doctor if you need to get a surveillance brain image. It needs to be a special brain imaging for brain aneurysms (for example a MRA or a CTA).
Not all brain images will show aneurysms.
Untreated brain aneurysms may rupture, resulting in a sudden headache that reaches its maximum intensity within seconds to minutes, often described as “worst headache of the life”, and it may be so severe that it causes blurry vision, neck pain, and even loss of consciousness.
It is considered a life-threatening emergency, and under that kind of circumstances 911 needs to be called immediately. Endovascular coiling procedure is a procedure to prevent brain aneurysms from bursting. A coiling procedure is used to block blood flow from flowing into the aneurysm from your brain’s arteries. By filling the affected area with tiny, soft plantinum coils, your neurosurgeon can essentially cut the aneurysm off from blood flow. The goals of coiling are to help prevent future bleeding.
You may ask yourself how coiling is performed. Coiling is a minimally invasive aneurysm treatment, but your doctor will most likely recommend general anesthesia to keep you immobile and prevent pain during the procedure. After you receive anesthesia, your neurosurgeons will make a small incision in your artery in the groin, or in some cases the incision can also be performed in your wrist area over the spot where you can feel your pulse. He or she will then thread a catheter, which is a small hollow and flexible tube, into your artery until it reaches the aneurysm.
A small amount of medical dye gets injected through the tube thereby “mapping” the way to the aneurysm, and two special X-ray cameras positioned outside your body will project that map onto big screens in a specialized operating room.
This is how the doctor advances the catheter to reach the aneurysm without damaging your artery.
If you have been told, you have an aneurysm, consider contacting Neurosurgeons of New Jersey to receive a 5-star consultation by one of our premier neurosurgeons.
Doctors at Neurosurgeons of NJ are also experts in performing coiling procedures through the wrist.
Once the aneurysm is reached, multiple small platinum coils get inserted into the aneurysm under direct visualization on multiple screens.
Those coils are inserted one at a time. Your neurosurgeon will determine the appropriate size and number of coils needed for a given aneurysm. Those coils compact to create a tiny metals ball, and that metal ball promotes blood clotting within the aneurysm. They prevent blood from entering the aneurysm. Without new blood being able to enter the aneurysm, the blood pressure that was pushing against the weak gets relieved and your aneurysm is considered cured.
In aneurysms with larger openings from the artery (known as “wide neck” aneurysms), your neurosurgeon may elect to use a balloon or other additional devices such as a metal stents which serve as a scaffold to keep the coils in place. If a stent is needed, you will require to take some medications for blood thinning.
Your neurosurgeon will instruct you what medicine would be best for your personal situation. Make sure to tell your neurosurgeons all medications you have been prescribed by other doctors or supplements you may be taking on your own. After you receive your coiling procedure, you will typically remain in the hospital for one to two days. During this time, nurses will monitor your progress to make sure you recover properly. They may also need to change bandages at the incision site.
Once released from the hospital, you need to avoid strenuous activities for at least seven days. It’s also wise to avoid driving during this time. You may shower, but do not submerge yourself in hot water. Assuming that your incision heals properly, you can return to your regular schedule in about 7 days.
If you notice any bleeding, swelling, discharge or other problems at the incision site, contact your doctor for advice.
He or she may want to readmit you to the hospital for a few days to monitor your progress. If The vast majority of people, however, recover easily from this procedure, and if you qualified for treatment through the wrist, your recovery is even easier. If you smoke, drink alcohol excessively or participate in other behaviors that increase the risk of getting an aneurysm, you may need to see your medical doctor about changing those unhealthy behaviors. Coiling can often correct aneurysms, but it’s important to lead a healthy lifestyle that helps prevent future complications. This part of your recovery may take several months or even years depending on your current state of health.

About Dr. Dorothea Altschul
Dr. Dorothea Altschul is an accomplished neurointerventionalist in North Jersey and is the Clinical Director of Endovascular Services at Neurosurgeons of New Jersey, practicing out of their Ridgewood office located on East Ridgewood Avenue.
Please call today to schedule a consultation with me.
(551) 284-3265
Request a consultation with Dr. Altschul