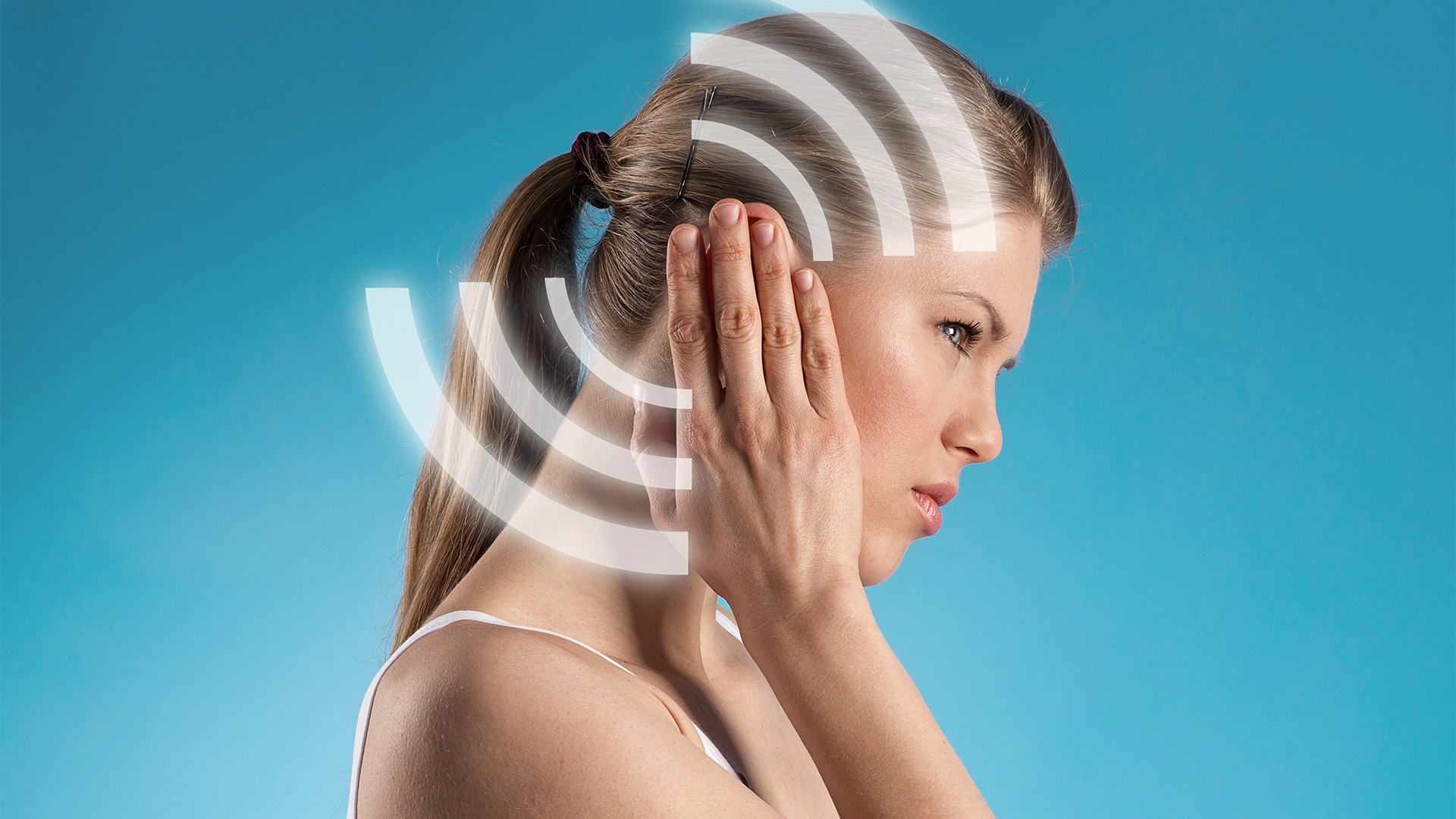
Hearing a rhythmic whooshing or heartbeat sound in your ear can be unsettling, especially when it’s persistent. Known as pulsatile tinnitus, this condition often creates anxiety and confusion as individuals try to understand what’s causing the sound. This guide will help you explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pulsatile tinnitus and discuss ways to manage the anxiety that can accompany it.
What is Pulsatile Tinnitus?
Pulsatile tinnitus is a form of tinnitus where you hear rhythmic noises that often sync with your heartbeat. Unlike typical tinnitus, which is characterized by a constant ringing or buzzing sound, pulsatile tinnitus has a distinct beat or pulsing rhythm. People may describe it as a “whooshing sound in the ear,” “heartbeat in the eardrum,” or even a “thumping sound in ear.”
This symptom can occur in one ear or both and may affect your daily activities and concentration. For some, it’s just an occasional sound; for others, it can be constant and distressing- so if you’re searching for terms such as ‘hear heart beat in ear’, or even ‘pulsing in ear’- you may find the answers you seek in this post.
Medical advice can be best pursued from a neurointerventional or cerebrovascular neurosurgeon, in the event a vascular cause has been identified.
Why Do I Feel My Heartbeat in My Head?
When you hear your heartbeat in your ear, it’s often due to blood flow changes near your ears or head. Blood vessels close to the middle ear are usually the cause, transmitting the beat of your pulse. Factors like high blood pressure, stress, and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) — abnormal connections between arteries and veins — can make this sound more noticeable.
The Tri-State's leaders
in Cerebrovascular treatments.
Is the Whooshing Sound in the Ear Dangerous?
While pulsatile tinnitus isn’t typically dangerous, it can sometimes indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention. Conditions such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), or issues in blood vessels around the ear might lead to pulsatile tinnitus. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help identify potential causes and determine if further evaluation, like imaging tests or a hearing test, is needed.
Common Symptoms of Pulsatile Tinnitus
Pulsatile tinnitus symptoms vary from person to person, but may include:
- A whooshing or heartbeat sound in the ear
- Fluttering sensation or ear thumping noise
- Ringing or pulsating sound in one or both ears
- Ear fluttering or feeling your heartbeat in your head
Some individuals may also experience anxiety, especially if they worry about the source or implications of the noise.
Can Stress Cause Pulsatile Tinnitus?
Yes, stress can play a role in both the onset and persistence of pulsatile tinnitus. Anxiety increases awareness of internal body sounds, making you more sensitive to hearing things like your heartbeat in your ears. This heightened awareness can create a cycle where tinnitus anxiety amplifies the sound, which in turn heightens anxiety further.
How Pulsatile Tinnitus and Anxiety Are Connected
Living with pulsatile tinnitus can be mentally taxing, especially when you are constantly aware of a noise that others don’t hear. Anxiety and mental health concerns can develop or worsen as people struggle with uncertainty about their health or worry that the sound might be a sign of something serious. An anxiety disorder can even contribute to worsening symptoms, as fear and hyperawareness make the sound feel louder or more intrusive.
For those who experience ringing in the ears or other tinnitus symptoms, managing anxiety can be as important as addressing the physical causes of the noise. Techniques like mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and sound therapy are effective in breaking the cycle of tinnitus anxiety and improving quality of life.
Treatment Options for Pulsatile Tinnitus
- Sound Generators and Maskers
Sound therapy can be beneficial, especially when tinnitus is stress-related. Devices called sound generators produce calming sounds to mask tinnitus. White noise machines, apps, and hearing aids with masking features are popular options that can make tinnitus less disruptive. - Hearing Tests and Medical Evaluation
Seeing a specialist for a hearing test and possibly imaging tests can help identify any treatable causes, especially if pulsatile tinnitus is related to blood vessels or the ear canal. If the source of the tinnitus is structural or vascular, addressing the root cause might relieve symptoms. - Stress and Anxiety Management
Since stress can worsen pulsatile tinnitus, learning to manage anxiety is key. Techniques like meditation, breathing exercises, and counseling can help. Mental health support may be especially helpful for breaking the feedback loop of anxiety and tinnitus. - Lifestyle Adjustments
Changes like reducing caffeine intake, avoiding loud noise exposure, and managing blood pressure can reduce the impact of pulsatile tinnitus. Regular physical activity and adequate hydration can also contribute to better vascular health, potentially reducing the intensity of the pulsating sound. - Medications and Therapies
Some patients benefit from medications aimed at controlling blood pressure or relaxing the muscles around the ear. Middle ear myoclonus (MEM), for example, is a rare condition involving spasms of tiny muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius) in the middle ear, which can create a rhythmic noise. Medications or botulinum toxin injections may be recommended if muscle spasms are the cause. - Neurointervention
This procedure is typically recommended when pulsatile tinnitus is linked to venous sinus stenosis—a narrowing of the venous channels that drain blood from the brain. By placing a stent within the narrowed venous sinus, blood flow is restored, relieving the turbulent blood flow that causes the pulsatile sound. For many, this results in a significant reduction or even elimination of symptoms. Venous sinus stenting offers hope for patients with otherwise difficult-to-treat pulsatile tinnitus, providing relief from this often life-disrupting condition.
When to Seek Medical Help
If pulsatile tinnitus persists, becomes more intense, or if you notice additional symptoms like dizziness or hearing loss, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. They can evaluate for conditions that might be causing or worsening the tinnitus. Sometimes, an issue with the ear canal, blood vessels, or even structural changes in the head and neck can create pulsatile tinnitus, and treatment may improve symptoms.
Conditions like high blood pressure and AVMs require monitoring, and treating them can reduce the pulsatile sound in your ear. Scheduling an appointment with a specialist can help rule out or confirm these potential causes.
Conclusion: Find Relief from Pulsatile Tinnitus
Pulsatile tinnitus is a common but often misunderstood symptom that can cause significant anxiety. Understanding potential causes, managing stress, and seeking medical advice are effective ways to address this condition. Whether it’s a lifestyle change, sound therapy, or a specific treatment plan, finding relief is possible. If pulsatile tinnitus is affecting your quality of life, reach out to a healthcare provider to explore the best options for your situation.

About Dr. Dorothea Altschul
Dr. Dorothea Altschul is an accomplished neurointerventionalist in North Jersey and is the Clinical Director of Endovascular Services at Neurosurgeons of New Jersey, practicing out of their Ridgewood office located on East Ridgewood Avenue.